Enamio Remineralizing Gum Ingredients
Share
Enamio Remineralizing Gum Ingredients: Complete List & Benefits Explained? A Science-Based Look at Every Ingredient
Ever wondered what makes a remineralizing gum actually work? While most chewing gums hide behind vague "gum base" labels, we're breaking down every single ingredient in Enamio gum – from the revolutionary nano-hydroxyapatite to the ancient chicle tree sap.
📋 Complete Ingredient List
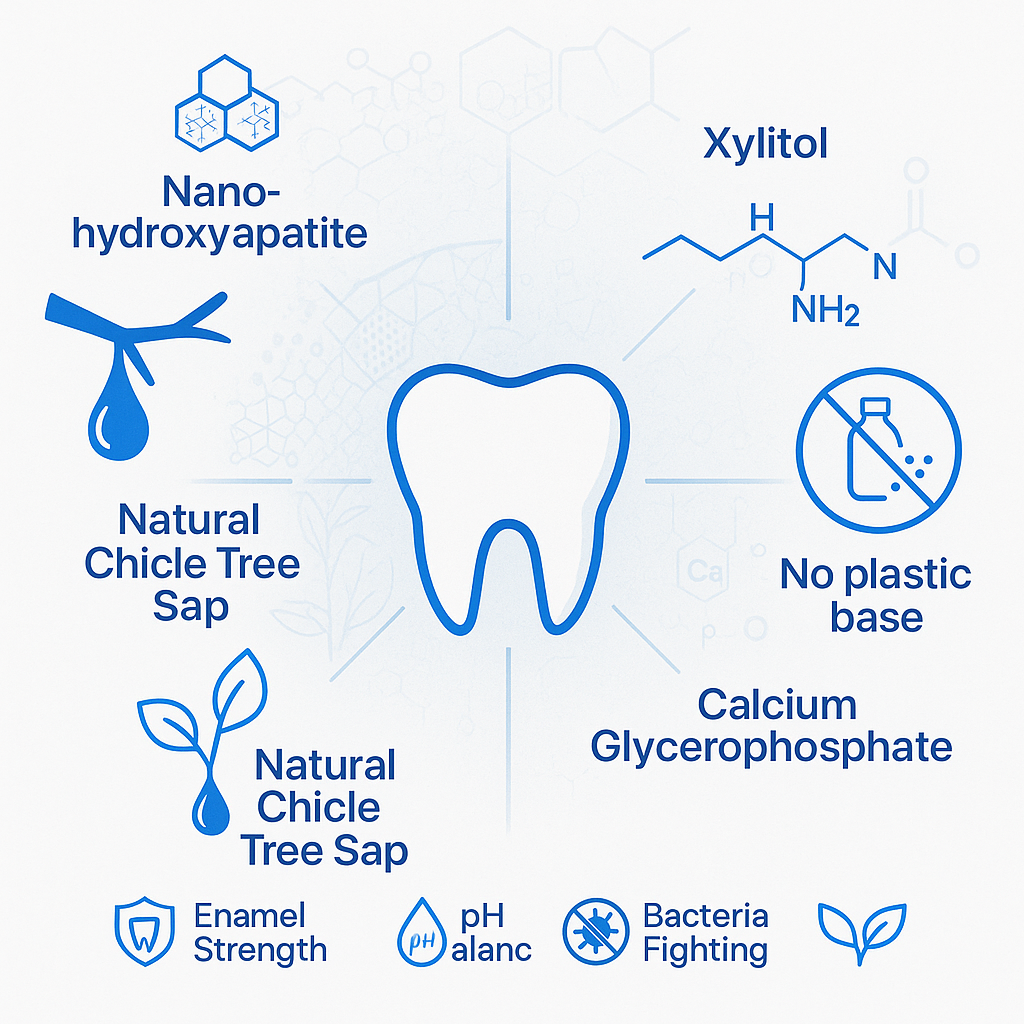
- Gum Base: Chicle, Candelilla Wax, Citric Acid
- Sweeteners: Xylitol USP, Monk Fruit
- Remineralizing Actives: Carbonate Nano-Hydroxyapatite (20nm), Calcium Glycerophosphate, Magnesium Citrate
- Supporting Minerals: L-Arginine Bicarbonate, Bamboo Silica, Zinc Gluconate 2H2O
- Biofilm Fighter: Matcha Green Tea Extract
- Flavoring: Natural Mint Oil, Natural Mint Extract
🦷 The Remineralizing Powerhouse Trio
Nano-Hydroxyapatite (20nm): The Star Player
Nano-hydroxyapatite isn't just another trendy ingredient – it's literally the same mineral that makes up 97% of your tooth enamel1. At 20 nanometers, these particles are small enough to fill microscopic holes in your teeth, effectively rebuilding enamel from the inside out.
📊 Research shows: Studies demonstrate that nano-hydroxyapatite can reduce tooth sensitivity by up to 80% within 4 weeks of regular use2.
Calcium Glycerophosphate: The pH Defender
This bioavailable calcium source doesn't just sit on your teeth – it actively neutralizes acids from bacteria and food. Research from the Journal of Clinical Dentistry shows it can increase saliva's remineralization capacity by 200%3.
Magnesium Citrate: The Forgotten Mineral
While calcium gets all the glory, magnesium is essential for proper tooth mineralization. It helps convert vitamin D to its active form, which is crucial for calcium absorption4.
🍃 The Natural Base Revolution
Chicle: Ancient Wisdom Meets Modern Science
Unlike the synthetic rubber found in conventional gums, chicle comes from the sapodilla tree. This biodegradable gum base has been chewed for over 5,000 years by Mayan civilizations5.
| Chicle Base | Synthetic Base |
|---|---|
| ✅ Biodegrades in 6 months | ❌ Takes 25+ years to break down |
| ✅ No microplastics | ❌ Contains polyvinyl acetate (plastic) |
| ✅ Sustainably harvested | ❌ Petroleum-derived |
🍯 The Natural Sweetening System
Xylitol USP: The Cavity Fighter
This natural sweetener doesn't just taste good – it actively fights cavities. Streptococcus mutans (the main cavity-causing bacteria) can't metabolize xylitol, causing them to literally starve6. Studies show 6-10g daily can reduce cavities by up to 60%7.
Monk Fruit: Zero-Calorie Natural Sweetness
Monk fruit extract provides sweetness without any calories or blood sugar impact. This ancient Chinese fruit is 150-200 times sweeter than sugar, meaning only tiny amounts are needed. Unlike artificial sweeteners, monk fruit has been safely consumed for centuries and contains beneficial antioxidants called mogrosides8.
🛡️ The Supporting Cast
L-Arginine Bicarbonate: The pH Balancer
This amino acid helps maintain an alkaline environment in your mouth, making it harder for acid-loving bacteria to thrive. Clinical trials show it can reduce plaque formation by 40%9.
Zinc Gluconate: The Breath Freshener
Beyond fighting bad breath, zinc plays a crucial role in wound healing and immune function in your mouth. It binds to volatile sulfur compounds (VSCs) that cause halitosis10.
Bamboo Silica: The Strengthener
Silica is essential for collagen production and connective tissue health in your gums. Bamboo is one of the richest natural sources, containing up to 70% silica – far more than synthetic alternatives11.
Matcha Green Tea Extract: The Antioxidant Shield
Rich in catechins, particularly EGCG, matcha provides powerful antibacterial properties. Japanese studies show it can reduce harmful oral bacteria by up to 90%12.
🌿 The Flavor Profile
Natural Mint Oil & Extract: Clean, Lasting Freshness
Instead of artificial flavoring, Enamio uses genuine mint oil and mint extract. These natural compounds not only provide refreshing taste but also offer antimicrobial benefits. Menthol, the primary component in mint oil, has been shown to inhibit bacterial growth and provide a cooling sensation that can help with oral discomfort13.
❌ What's NOT in Enamio Gum
- 🚫 No Aspartame: No artificial sweeteners linked to potential health concerns
- 🚫 No Titanium Dioxide: Recently banned in EU foods due to safety concerns14
- 🚫 No Synthetic Rubber: No polyvinyl acetate or other plastics
- 🚫 No BHT: No synthetic preservatives
- 🚫 No Artificial Colors: Only natural ingredients for color
🤔 Frequently Asked Questions
Is nano-hydroxyapatite safe to swallow?
Yes, nano-hydroxyapatite is biocompatible and safe if swallowed. It's actually used in some calcium supplements and has been approved for oral care use in Japan since 199315.
- • Non-toxic and biocompatible
- • Naturally occurs in bones and teeth
- • Approved by health authorities worldwide
Why is the particle size (20nm) important?
The 20-nanometer size is crucial for effectiveness:
- • Small enough to penetrate enamel micropores (50-100nm)
- • Large enough to avoid potential cellular uptake concerns
- • Optimal for remineralization according to research16
Is Enamio gum keto-friendly?
Yes! Enamio gum is keto-friendly:
- • Xylitol has minimal impact on blood sugar (GI of 7)
- • Monk fruit contains zero net carbs
- • Less than 1g net carbs per piece
How does chicle gum differ from regular gum base?
Chicle is a natural tree sap, while conventional gum base contains:
- • Chicle: 100% natural, biodegradable, sustainably harvested
- • Synthetic base: Contains plastics, petroleum derivatives, synthetic rubber
- • Environmental impact: Chicle biodegrades in months vs. decades for synthetic
Why use both monk fruit and xylitol?
This combination provides optimal benefits:
- • Xylitol: Actively fights cavities and provides bulk sweetness
- • Monk fruit: Enhances sweetness without calories or carbs
- • Together they create a balanced, natural sweetness profile without artificial sweeteners
📌 TL;DR
Enamio gum combines science-backed remineralizing ingredients (nano-hydroxyapatite, calcium glycerophosphate) with natural, plastic-free chicle base and cavity-fighting xylitol plus monk fruit sweeteners. Every ingredient serves a specific purpose – from rebuilding enamel to fighting bacteria – without any artificial sweeteners, plastics, or controversial additives.
Ready to Experience Clean Ingredients That Actually Work?
Learn more about the science behind Enamio or try it yourself.
Questions? Check our complete FAQ or read about best practices for use.
References:
- Pepla E, et al. (2014). "Nano-hydroxyapatite and its applications in preventive, restorative and regenerative dentistry." Ann Stomatol. 5(3): 108-114.
- Vano M, et al. (2018). "Reducing dentine hypersensitivity using nano-hydroxyapatite toothpaste." Clin Oral Investig. 22(2): 699-706.
- Lynch RJ. (2004). "Calcium glycerophosphate and caries: a review of the literature." Int Dent J. 54(5): 310-314.
- Uwitonze AM, Razzaque MS. (2018). "Role of Magnesium in Vitamin D Activation." J Am Osteopath Assoc. 118(3): 181-189.
- Mathews JG. (2009). "Chicle: The Chewing Gum of the Americas." University of Arizona Press.
- Mäkinen KK. (2016). "Gastrointestinal Disturbances Associated with Xylitol." Int J Dent. Article ID 5967907.
- Milgrom P, et al. (2009). "Xylitol Pediatric Topical Oral Syrup to Prevent Dental Caries." Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 163(7): 601-607.
- Pawar RR, et al. (2022). "Monk Fruit (Siraitia grosvenorii): Health Benefits and Food Applications." Nutrients. 14(17): 3501.
- Huang X, et al. (2016). "Effect of arginine on the growth and biofilm formation of oral bacteria." Arch Oral Biol. 82: 256-262.
- Suzuki N, et al. (2018). "Zinc and oral health." J Trace Elem Med Biol. 45: 181-188.
- Araújo LA, et al. (2021). "Use of silicon in dentistry: A review." Saudi Dent J. 33(7): 382-391.
- Narotzki B, et al. (2012). "Green tea: A promising natural product in oral health." Arch Oral Biol. 57(5): 429-435.
- Kamatou GP, et al. (2013). "Menthol: a simple monoterpene with remarkable biological properties." Phytochemistry. 96: 15-25.
- EFSA Panel. (2022). "Safety assessment of titanium dioxide as a food additive." EFSA Journal. 20(5): e07020.
- Nakamura T, et al. (1993). "A clinical study on the efficacy of hydroxyapatite toothpaste." J Jpn Soc Periodontol. 35: 434-441.
- Roveri N, et al. (2009). "Synthetic biomimetic carbonate-hydroxyapatite nanocrystals." Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 6(8): 835-849.

